Fill a Valid IRS 1099-MISC Form
The IRS 1099-MISC form plays a crucial role in the world of taxation, particularly for independent contractors, freelancers, and businesses that engage in non-employee compensation. This form is used to report various types of income that aren’t classified as wages, salaries, or tips. It captures payments made to individuals or entities that provide services, including legal fees, rents, and prizes, among others. For many, receiving a 1099-MISC means they must take a closer look at their tax obligations, as the income reported on this form is typically taxable. Understanding how to fill out the 1099-MISC accurately is essential for both payers and recipients to ensure compliance with IRS regulations. Furthermore, the form's requirements have evolved over the years, so staying informed about the latest changes is vital for anyone involved in reporting or receiving miscellaneous income. Whether you’re a business owner or a self-employed individual, grasping the nuances of the 1099-MISC can make tax season a lot less daunting.
Additional PDF Templates
W-9 Fillable 2023 - Filling out a W-9 is straightforward, requiring basic identification details.
When dealing with the sale of a recreational vehicle, having the correct documentation is vital. The Georgia RV Bill of Sale form not only formalizes the ownership transfer but also acts as a critical receipt for the transaction. For more information and to access the form, you can visit https://georgiapdf.com/rv-bill-of-sale/, ensuring that both parties have their details in order for a smooth sale.
Cdph Tb Risk Assessment - Patients may require this form for school or job requirements.
Similar forms
The IRS 1099-MISC form is used to report various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips. Several other forms serve similar purposes, each designed to capture specific types of payments. Here are ten documents that share similarities with the 1099-MISC form:
- 1099-NEC: This form is specifically used to report nonemployee compensation, which was previously reported on the 1099-MISC. It captures payments made to independent contractors.
- 1099-INT: This form reports interest income earned by individuals. Like the 1099-MISC, it informs the IRS of income that may not come from employment.
- Living Will: The All Ohio Forms include a legal document that allows individuals to specify their medical treatment preferences when they cannot make decisions themselves.
- 1099-DIV: Used for reporting dividends and distributions, this form also informs the IRS about income received from investments, similar to how the 1099-MISC reports various payments.
- 1099-G: This form is used to report certain government payments, such as unemployment compensation. It parallels the 1099-MISC in that it reports income not derived from traditional employment.
- 1099-R: This form reports distributions from retirement accounts. Like the 1099-MISC, it serves to inform the IRS about payments made outside of regular wages.
- W-2: While primarily for reporting wages, the W-2 form also includes information about other types of compensation and benefits. It contrasts with the 1099-MISC by focusing on employee income.
- Schedule K-1: This form reports income, deductions, and credits from partnerships, S corporations, estates, and trusts. It shares the purpose of informing the IRS about income received by individuals.
- Form 1098: This document reports mortgage interest paid, helping taxpayers claim deductions. It is similar in that it reports financial information relevant to tax obligations.
- Form 1099-C: This form is used to report cancellation of debt. Like the 1099-MISC, it highlights income that may not be immediately obvious to the taxpayer.
- Form 1099-S: This form reports proceeds from real estate transactions. It serves a similar function to the 1099-MISC by documenting income from non-employment sources.
Understanding these forms can help ensure compliance with tax reporting requirements and avoid potential issues with the IRS.
Document Example

Attention:
Copy A of this form is provided for informational purposes only. Copy A appears in red, similar to the official IRS form. The official printed version of Copy A of this IRS form is scannable, but the online version of it, printed from this website, is not. Do not print and file copy A downloaded from this website; a penalty may be imposed for filing with the IRS information return forms that can’t be scanned. See part O in the current General Instructions for Certain Information Returns, available at IRS.gov/Form1099, for more information about penalties.
Please note that Copy B and other copies of this form, which appear in black, may be downloaded and printed and used to satisfy the requirement to provide the information to the recipient.
If you have 10 or more information returns to file, you may be required to file
If you have fewer than 10 information returns to file, we strongly encourage you to
See Publications 1141, 1167, and 1179 for more information about printing these forms.
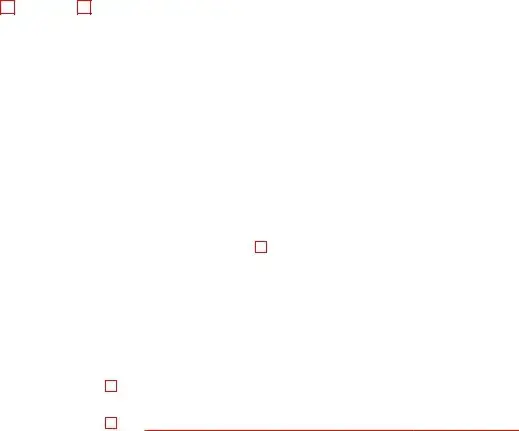
9595 |
|
VOID |
CORRECTED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
PAYER’S name, street address, city or town, state or province, country, ZIP |
1 |
Rents |
OMB No. |
|
|
|||||||
or foreign postal code, and telephone no. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
Form |
|
Miscellaneous |
||||
|
|
|
|
2 |
Royalties |
(Rev. January 2024) |
|
Information |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
For calendar year |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Other income |
4 |
Federal income tax withheld |
Copy A |
||||
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
For |
|
PAYER’S TIN |
RECIPIENT’S TIN |
|
5 |
Fishing boat proceeds |
6 |
Medical and health care |
Internal Revenue |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
payments |
Service Center |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
File with Form 1096. |
|
RECIPIENT’S name |
|
|
7 |
Payer made direct sales |
8 |
Substitute payments in lieu |
For Privacy Act |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
totaling $5,000 or more of |
|
of dividends or interest |
and Paperwork |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
consumer products to |
$ |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
recipient for resale |
|
|
|
|
Reduction Act |
||
Street address (including apt. no.) |
|
|
9 |
Crop insurance proceeds |
10 |
Gross proceeds paid to an |
Notice, see the |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
attorney |
current General |
||||
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
Instructions for |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Certain |
|||
City or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code |
11 |
Fish purchased for resale |
12 |
Section 409A deferrals |
||||||||
Information |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
Returns. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
13 FATCA filing |
14 |
Excess golden parachute |
15 |
Nonqualified deferred |
|
||||
|
|
|
requirement |
|
payments |
|
compensation |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Account number (see instructions) |
|
|
2nd TIN not. |
16 |
State tax withheld |
17 |
State/Payer’s state no. |
18 State income |
||||
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
Form |
Cat. No. 14425J |
www.irs.gov/Form1099MISC |
|
Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service |
||||||||
Do Not Cut or Separate Forms on This Page — Do Not Cut or Separate Forms on This Page

|
VOID |
CORRECTED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
PAYER’S name, street address, city or town, state or province, country, ZIP |
1 |
Rents |
OMB No. |
|
|
|
|||||
or foreign postal code, and telephone no. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
Form |
|
Miscellaneous |
||||
|
|
|
2 |
Royalties |
(Rev. January 2024) |
|
|
Information |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
For calendar year |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Other income |
4 |
Federal income tax withheld |
|
Copy 1 |
|||
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
For State Tax |
PAYER’S TIN |
RECIPIENT’S TIN |
|
5 |
Fishing boat proceeds |
6 |
Medical and health care |
|
Department |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
payments |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RECIPIENT’S name |
|
|
7 |
Payer made direct sales |
8 |
Substitute payments in lieu |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
totaling $5,000 or more of |
|
of dividends or interest |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
consumer products to |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
recipient for resale |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Street address (including apt. no.) |
|
|
9 |
Crop insurance proceeds |
10 |
Gross proceeds paid to an |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
attorney |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
City or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code |
11 |
Fish purchased for resale |
12 |
Section 409A deferrals |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 FATCA filing |
14 |
Excess golden parachute |
15 |
Nonqualified deferred |
|
|
|||
|
|
requirement |
|
payments |
|
compensation |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Account number (see instructions) |
|
|
16 |
State tax withheld |
17 |
State/Payer’s state no. |
|
18 State income |
|||
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
Form |
|
www.irs.gov/Form1099MISC |
|
Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service |
|||||||
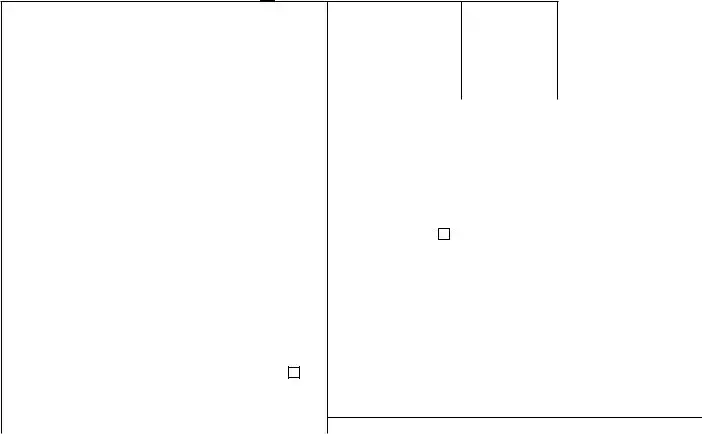

 CORRECTED (if checked)
CORRECTED (if checked)
PAYER’S name, street address, city or town, state or province, country, ZIP 1 Rents |
OMB No. |
or foreign postal code, and telephone no. |
|
|
|
|
$ |
Form |
Miscellaneous |
|||||
|
|
|
2 Royalties |
(Rev. January 2024) |
|
|
Information |
|||
|
|
|
|
For calendar year |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
3 Other income |
4 Federal income tax withheld |
Copy B |
|||||
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
For Recipient |
PAYER’S TIN |
RECIPIENT’S TIN |
5 Fishing boat proceeds |
6 |
Medical and health care |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
payments |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RECIPIENT’S name |
|
|
7 Payer made direct sales |
8 |
Substitute payments in lieu |
|
This is important tax |
|||
|
|
|
totaling $5,000 or more of |
|
of dividends or interest |
|
||||
|
|
|
consumer products to |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
information and is |
|
|
|
recipient for resale |
|
|
|
|
|
being furnished to |
|
Street address (including apt. no.) |
|
|
9 Crop insurance proceeds |
10 |
Gross proceeds paid to an |
|
the IRS. If you are |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
attorney |
|
required to file a |
|||
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
return, a negligence |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
penalty or other |
||
City or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code |
11 Fish purchased for resale |
12 |
Section 409A deferrals |
|
sanction may be |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
imposed on you if |
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
this income is |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
taxable and the IRS |
||
|
|
13 FATCA filing 14 Excess golden parachute |
15 |
Nonqualified deferred |
|
determines that it |
||||
|
|
requirement |
payments |
|
compensation |
|
has not been |
|||
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
reported. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Account number (see instructions) |
|
|
16 State tax withheld |
17 |
State/Payer’s state no. |
|
18 State income |
|||
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
Form |
(keep for your records) |
www.irs.gov/Form1099MISC |
|
Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service |
||||||
Instructions for Recipient
Recipient’s taxpayer identification number (TIN). For your protection, this form may show only the last four digits of your social security number (SSN), individual taxpayer identification number (ITIN), adoption taxpayer identification number (ATIN), or employer identification number (EIN). However, the payer has reported your complete TIN to the IRS.
Account number. May show an account or other unique number the payer assigned to distinguish your account.
Amounts shown may be subject to
Form
Box 1. Report rents from real estate on Schedule E (Form 1040). However, report rents on Schedule C (Form 1040) if you provided significant services to the tenant, sold real estate as a business, or rented personal property as a business. See Pub. 527.
Box 2. Report royalties from oil, gas, or mineral properties; copyrights; and patents on Schedule E (Form 1040). However, report payments for a working interest as explained in the Schedule E (Form 1040) instructions. For royalties on timber, coal, and iron ore, see Pub. 544.
Box 3. Generally, report this amount on the “Other income” line of Schedule 1 (Form 1040) and identify the payment. The amount shown may be payments received as the beneficiary of a deceased employee, prizes, awards, taxable damages, Indian gaming profits, or other taxable income. See Pub. 525. If it is trade or business income, report this amount on Schedule C or F (Form 1040).
Box 4. Shows backup withholding or withholding on Indian gaming profits. Generally, a payer must backup withhold if you did not furnish your TIN. See Form
Box 5. Shows the amount paid to you as a fishing boat crew member by the operator, who considers you to be
Box 6. For individuals, report on Schedule C (Form 1040).
Box 7. If checked, consumer products totaling $5,000 or more were sold to you for resale, on a
Box 8. Shows substitute payments in lieu of dividends or
Box 9. Report this amount on Schedule F (Form 1040).
Box 10. Shows gross proceeds paid to an attorney in connection with legal services. Report only the taxable part as income on your return.
Box 11. Shows the amount of cash you received for the sale of fish if you are in the trade or business of catching fish.
Box 12. May show current year deferrals as a nonemployee under a nonqualified deferred compensation (NQDC) plan that is subject to the requirements of section 409A plus any earnings on current and prior year deferrals.
Box 13. If the FATCA filing requirement box is checked, the payer is reporting on this Form 1099 to satisfy its account reporting requirement under chapter 4 of the Internal Revenue Code. You may also have a filing requirement. See the Instructions for Form 8938.
Box 14. Shows your total compensation of excess golden parachute payments subject to a 20% excise tax. See your tax return instructions for where to report.
Box 15. Shows income as a nonemployee under an NQDC plan that does not meet the requirements of section 409A. Any amount included in box 12 that is currently taxable is also included in this box. Report this amount as income on your tax return. This income is also subject to a substantial additional tax to be reported on Form 1040,
Boxes
Future developments. For the latest information about developments related to Form
Free File Program. Go to www.irs.gov/FreeFile to see if you qualify for
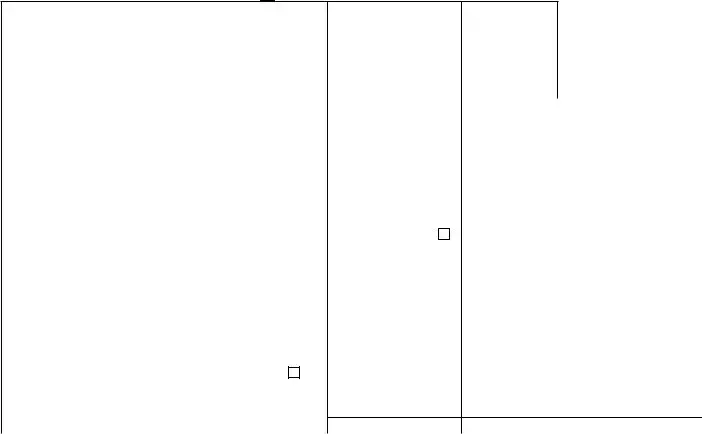

 CORRECTED (if checked)
CORRECTED (if checked)
PAYER’S name, street address, city or town, state or province, country, ZIP 1 Rents |
OMB No. |
or foreign postal code, and telephone no. |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
Form |
Miscellaneous |
|||||
|
|
|
2 Royalties |
|
(Rev. January 2024) |
|
|
Information |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
For calendar year |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
3 Other income |
4 |
Federal income tax withheld |
|
Copy 2 |
||||
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
To be filed with |
|
PAYER’S TIN |
RECIPIENT’S TIN |
5 Fishing boat proceeds |
6 |
Medical and health care |
|
recipient’s state |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
payments |
|
income tax return, |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
when required. |
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RECIPIENT’S name |
|
|
7 Payer made direct sales |
8 |
Substitute payments in lieu |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
totaling $5,000 or more of |
|
|
of dividends or interest |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
consumer products to |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
recipient for resale |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Street address (including apt. no.) |
|
|
9 Crop insurance proceeds |
10 |
Gross proceeds paid to an |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
attorney |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code |
11 Fish purchased for resale |
12 |
Section 409A deferrals |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 FATCA filing 14 Excess golden parachute |
15 |
Nonqualified deferred |
|
|
|||||
|
|
requirement |
payments |
|
|
compensation |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Account number (see instructions) |
|
|
16 State tax withheld |
17 |
State/Payer’s state no. |
|
18 State income |
||||
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
Form |
www.irs.gov/Form1099MISC |
|
|
Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service |
|||||||
Form Specs
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS 1099-MISC form is used to report various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips. |
| Who Receives It | Individuals and businesses that receive $600 or more in non-employee compensation must receive a 1099-MISC form. |
| Filing Deadline | The deadline for filing the 1099-MISC form with the IRS is typically January 31 of the following year. |
| State-Specific Forms | Some states require their own forms for reporting income. For example, California requires Form 1099-MISC to comply with California Revenue and Taxation Code Section 18661. |
| Penalties | Failure to file the 1099-MISC on time can result in penalties, which increase based on how late the form is submitted. |
Crucial Questions on This Form
- Independent contractors
- Freelancers
- Rent payments
- Prizes and awards
- Other types of income
- The recipient's name and address
- The recipient's taxpayer identification number (TIN), which can be their Social Security number or Employer Identification Number
- The amount paid during the tax year
- Your business information, including name, address, and TIN
What is the IRS 1099-MISC form?
The IRS 1099-MISC form is used to report various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips. It is typically issued to independent contractors, freelancers, and other non-employees who have received payments for services rendered. This form helps the IRS track income that may not be reported on a W-2 form.
Who needs to file a 1099-MISC?
If you have paid someone $600 or more for services in a calendar year, you are generally required to file a 1099-MISC for that individual or business. This includes payments made to:
When is the 1099-MISC form due?
The 1099-MISC form must be filed by January 31 of the year following the tax year in which the payments were made. If you are filing electronically, the deadline remains the same. However, if you are submitting paper forms, the IRS requires them to be postmarked by the same date.
What information is needed to complete the 1099-MISC?
To complete the 1099-MISC, you will need the following information:
What should I do if I made a mistake on the 1099-MISC?
If you discover an error after filing the 1099-MISC, you should issue a corrected form. To do this, complete a new 1099-MISC with the correct information and check the box indicating that it is a corrected form. Send the corrected form to the recipient and the IRS as soon as possible.
What happens if I don’t file a 1099-MISC?
Failing to file a 1099-MISC when required can result in penalties from the IRS. These penalties can vary based on how late the form is filed. It is crucial to comply with filing requirements to avoid potential fines and complications with your tax reporting.
Can I file the 1099-MISC electronically?
Yes, you can file the 1099-MISC electronically. The IRS encourages electronic filing, especially for businesses that need to submit multiple forms. You can use the IRS e-file system or third-party software to file electronically. Ensure that you follow all guidelines to avoid issues.
Where can I obtain the 1099-MISC form?
The 1099-MISC form can be obtained from the IRS website or through various tax software programs. It is important to use the official IRS version of the form, as photocopies or printed versions may not be accepted by the IRS. You can also request physical copies from the IRS if needed.
Documents used along the form
The IRS 1099-MISC form is essential for reporting various types of income, but it often accompanies other important documents. Understanding these related forms can help ensure accurate reporting and compliance with tax regulations. Below are six commonly used forms and documents that complement the 1099-MISC.
- W-9 Form: This form is used by individuals and businesses to provide their taxpayer identification number (TIN) to the entity requesting it. The information collected helps the payer accurately report payments to the IRS.
- 1099-NEC Form: Introduced in 2020, this form specifically reports nonemployee compensation. It is used for payments made to independent contractors and freelancers, ensuring that these earnings are reported separately from other types of income.
- Schedule C: Self-employed individuals use this form to report income and expenses from their business. It provides a detailed overview of earnings, which can help in determining taxable income.
- Form 1040: This is the standard individual income tax return form. Taxpayers report their total income, including amounts from the 1099-MISC, and calculate their tax liability on this form.
- Form 1096: This form serves as a summary of all 1099 forms filed for a particular tax year. It is required when submitting paper copies of 1099 forms to the IRS, providing a comprehensive overview of the reported payments.
- Power of Attorney Form: For those needing to authorize someone to act on their behalf, consider the essential Power of Attorney document resources to ensure your wishes are legally upheld.
- State Tax Forms: Depending on the state, additional forms may be required for reporting income. These forms vary by state and may include state-specific 1099 forms or income tax returns.
Being aware of these documents can streamline the tax reporting process and help ensure compliance with IRS requirements. Properly managing these forms will ultimately lead to a smoother experience during tax season.
Misconceptions
The IRS 1099-MISC form is often misunderstood. Here are some common misconceptions that can lead to confusion:
- All payments require a 1099-MISC form. Many people believe that any payment made to an independent contractor or vendor must be reported using this form. However, only payments that total $600 or more in a calendar year for services rendered typically need to be reported. Smaller amounts do not require a 1099-MISC.
- 1099-MISC is the only form for reporting income. Some individuals think that the 1099-MISC is the only way to report non-employee compensation. In fact, starting in the tax year 2020, the IRS introduced the 1099-NEC form specifically for reporting non-employee compensation. The 1099-MISC is still used for other types of payments, such as rent or prizes.
- Receiving a 1099-MISC means you owe taxes. It’s a common belief that receiving this form automatically means you will owe taxes. While it does indicate that income was reported to the IRS, it does not necessarily mean you will owe taxes. Various deductions and credits may apply, which can reduce your tax liability.
- Only businesses need to issue 1099-MISC forms. Many assume that only corporations or businesses are responsible for issuing this form. In reality, any individual or entity that pays $600 or more for services must issue a 1099-MISC, regardless of whether they are a business or an individual.
Understanding these misconceptions can help ensure that you are accurately reporting income and complying with tax regulations. If you have further questions, consulting a tax professional is always a wise choice.
